It is the 21st century and it is no doubt that our phones are listening to us; data collection has become one of the biggest businesses in the world now. Have you ever wondered why that torchlight app on your phone needs access to your contacts for? With emerging Artificial Intelligent (AI) systems and algorithms, it is evident that user data has become the “fuel” of the digital space.
With this in mind, it is eminent that we scrutinize the amount of data we are giving out, the type of data, how long it will be stored, and what these data will be used for by tech firms and app developers.
The rise of AI has carried along with it ethical issues that deals with how user data is handled. Given this, a lot of technology laws have been instituted by international bodies to companies and developers to ensure that they are accountable to the privacy of user data as well as respecting the rights of users. Before delving into technology research journalism, app privacy and permissions was one area I had taken for granted until I started researching about the impact of the data we give away as users of technology and ways in which we can be prone to data hacks and exploitation if we act unconcerned.
The android operating system is one that has been loved by many because it makes room for easy customization, operationalization and forthright instruction. From fitness tracking apps to graphic demanding games, the smartphone ecosystem is made possible due to applications which may run as system or user defined.

Starting with Android version 6.0, the ability for users to take greater control of what kind of information they are giving out had been streamlined to make it easier to deal with. Before this development, earlier versions of the operating system did not give users an option to take control of what permissions apps were demanding. In earlier versions of android, the only way of avoiding an application having access to certain user data that was deemed not needed in the app’s operation was to completely avoid installing it in the very first place. This was an unpleasant issue because it meant that if you had for instance a favourite weather app in your play store that needed access to your SMS , the only way you could deny access to the app having that particular permission was to avoid installing it. Later developments removed this restriction by allowing users to consent and deny permissions at will.
Purposes of app permissions
App permissions are in place to make sure that your interaction with an app is smooth and seamless, for instance an app like whatsapp on reasonable grounds, needs access to your phone’s camera, storage and microphone in order for it to function effectively. However, this is where some developers overstep their boundaries and ask for data that is not related to how an app functions.
The process of curtailing the information fed to apps is fairly simple on devices running Android 6..0 and later,The process is outlined below:
- Go to settings
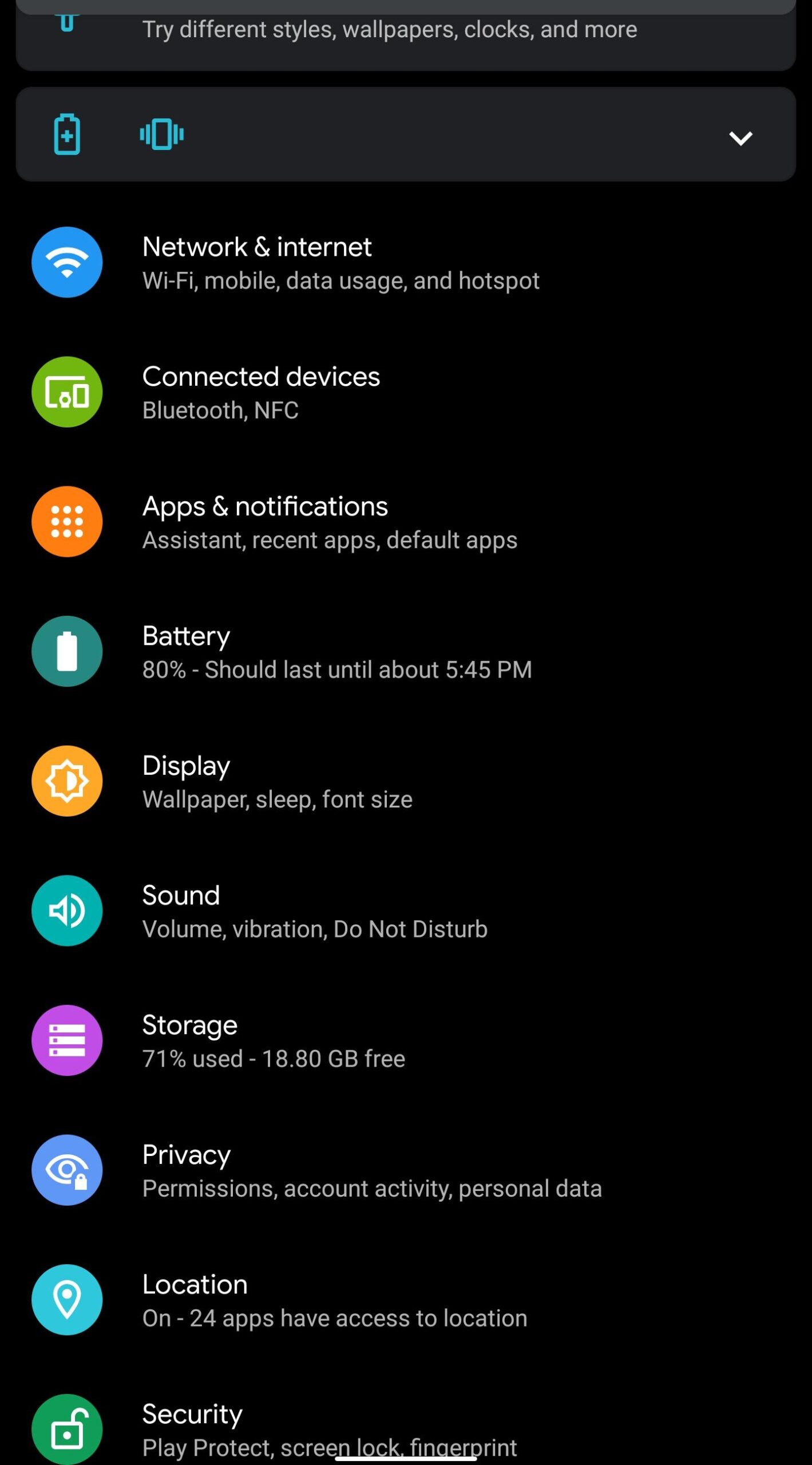
2.Search for all apps

3 Zero in on the specific app you would want to take charge off

4. Select the app
 5.Beneath it you will find a list that shows all the types of permissions being requested by the app
5.Beneath it you will find a list that shows all the types of permissions being requested by the app

From there, you can toggle the desired option ‘on and off’.
NB some permissions are fundamental to the operation of certain apps. Truth is that one must apply some level of wisdom and discretion and also find out if the data being requested is in congruence with the app’s performance, if not quickly revoke it.
I guess from this educational piece, you have now learnt not to always tap the allow button whenever you install a new app. Just imagine the chances of a malicious app being able to access your private messages, videos and pictures which could have been easily avoided with just a simple toggle away.
Take charge! as an individual, you have rights to privacy online. Know them and rightly apply the knowledge in protecting yourself in a data-hungry era.
Image Sources:
1) dhakatribune.com
2) Techrounder.com